Hawaii, renowned for its breathtaking landscapes, vibrant culture, and unique biodiversity, has long been a top destination for tourists from around the world. However, the question arises: can Hawaii survive without tourism? To answer this, we need to explore the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism on Hawaii and consider the alternatives available to sustain its economy.
The Role of Tourism in Hawaii’s Economy
Tourism is a cornerstone of Hawaii’s economy. In 2019, before the pandemic, tourism brought in $17.75 billion in visitor spending, supporting over 216,000 jobs and contributing significantly to state and local tax revenues. The pandemic, however, highlighted the vulnerability of this dependency, as travel restrictions and lockdowns led to a sharp decline in tourism and, consequently, economic hardship for many residents.
Economic Dependence
Tourism accounts for approximately 21% of Hawaii’s economy. This heavy reliance means that any downturn in visitor numbers can have drastic effects on employment, business revenue, and government budgets. For instance, hotels, restaurants, and retail stores heavily depend on tourists for their revenue, and many of these establishments suffered severe losses during the pandemic.
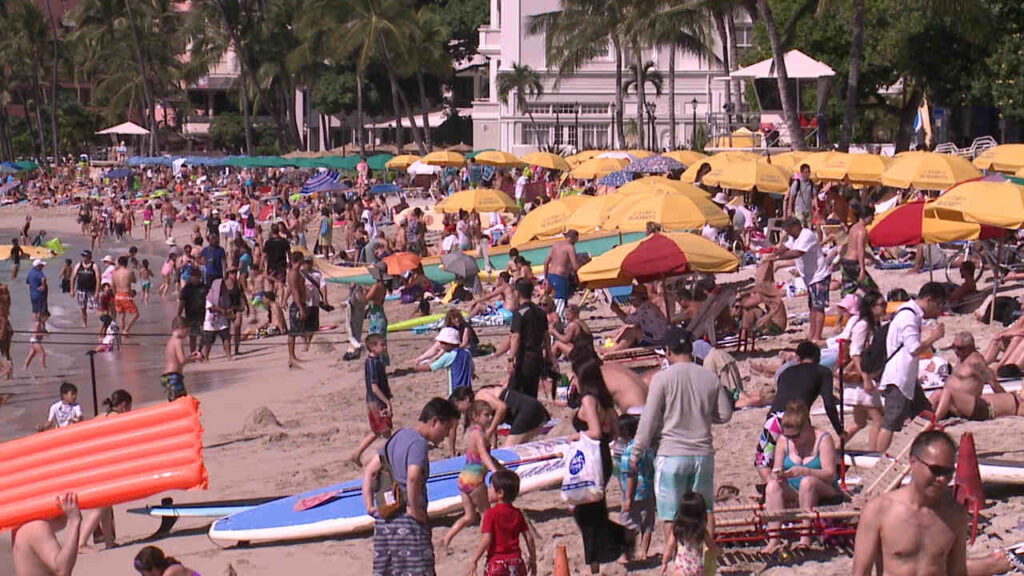
Job Market Impact
The tourism industry is a major employer in Hawaii, offering jobs in sectors like hospitality, food service, transportation, and entertainment. A decline in tourism directly impacts these jobs, leading to higher unemployment rates and economic instability.
Potential Alternatives to Tourism
While tourism is vital to Hawaii’s economy, there are several potential alternatives that could be developed to reduce dependence on this single industry.
Diversification into Agriculture
Hawaii has a rich agricultural history, and revitalizing this sector could provide economic stability. Investing in sustainable farming practices, promoting local produce, and exporting unique Hawaiian products like coffee, macadamia nuts, and tropical fruits could offer significant economic benefits.
Renewable Energy
Hawaii’s geographical location makes it ideal for renewable energy projects. Investing in solar, wind, and geothermal energy could not only create jobs but also reduce energy costs and promote sustainability. Hawaii aims to generate 100% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2045, which could become a significant economic driver.
Technology and Innovation
Promoting Hawaii as a hub for technology and innovation could attract businesses and skilled workers. Establishing tech parks, offering tax incentives for startups, and fostering partnerships with educational institutions could diversify the economy and create high-paying jobs.
Film and Television Production
Hawaii’s diverse landscapes make it an attractive location for film and television production. Expanding this industry could create jobs, stimulate local businesses, and promote Hawaii as a cultural icon globally.
Cultural and Educational Tourism
While traditional tourism focuses on leisure, promoting cultural and educational tourism could attract visitors interested in learning about Hawaiian history, culture, and the environment. This could be done sustainably, with a focus on preserving Hawaii’s natural and cultural heritage.
Environmental and Social Considerations
Reducing dependence on tourism could also have positive environmental and social impacts. Tourism can lead to overdevelopment, strain on natural resources, and environmental degradation. By diversifying the economy, Hawaii could implement more sustainable practices and reduce the environmental footprint associated with mass tourism.
Environmental Preservation
With fewer tourists, there would be less strain on natural resources, leading to better preservation of Hawaii’s unique ecosystems. This could help protect endangered species, coral reefs, and pristine landscapes that are currently under threat from overuse and pollution.
Social Benefits
A diversified economy could lead to improved quality of life for residents by providing stable, well-paying jobs outside the volatile tourism sector. This stability could reduce social issues such as poverty and homelessness, which are exacerbated by economic downturns in tourism.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is Hawaii so dependent on tourism?

Hawaii’s natural beauty, unique culture, and year-round pleasant climate make it a prime destination for tourists. Over the decades, the state has heavily invested in developing its tourism infrastructure, making it a major economic driver.
2. What are the risks of being overly dependent on tourism?
Economic dependency on tourism makes Hawaii vulnerable to global events that can disrupt travel, such as pandemics, economic recessions, and natural disasters. This can lead to high unemployment rates and economic instability.
3. Can agriculture really replace tourism in Hawaii?
While agriculture alone may not fully replace tourism, it can significantly contribute to economic diversification. With investments in technology and sustainable practices, agriculture can become a substantial economic sector.
4. How can Hawaii attract tech companies and startups?
Hawaii can attract tech companies by offering tax incentives, creating tech parks, and fostering partnerships with educational institutions. The state’s unique environment and quality of life can also be selling points for attracting skilled workers.
5. What are the environmental benefits of reducing tourism?
Reducing tourism can lead to less environmental degradation, better preservation of natural resources, and reduced carbon emissions. This can help protect Hawaii’s unique ecosystems and biodiversity.
6. Are there successful examples of places that have reduced their reliance on tourism?
Yes, several regions around the world have successfully diversified their economies to reduce reliance on tourism. For example, Iceland has invested heavily in renewable energy, and Singapore has developed a strong finance and technology sector.
7. What role does education play in economic diversification?
Education is crucial for economic diversification as it provides the skilled workforce needed for new industries. By investing in education, Hawaii can develop talent in fields like technology, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture.
8. How can residents contribute to economic diversification?
Residents can support local businesses, participate in community planning, and advocate for policies that promote economic diversification. Education and retraining programs can also help residents transition to jobs in new industries.
9. What is the government’s role in reducing tourism dependency?
The government can play a key role by creating policies and incentives to attract new industries, investing in infrastructure, and supporting education and training programs. Public-private partnerships can also be crucial in driving diversification efforts.
10. Is it possible to achieve a balance between tourism and other industries?
Yes, achieving a balance is possible and desirable. A diversified economy can provide stability and resilience, while sustainable tourism practices can continue to bring in revenue without overwhelming the environment or community resources.
Conclusion
While tourism will likely remain an important part of Hawaii’s economy, reducing its dependency on this single industry is crucial for long-term sustainability and resilience. By investing in agriculture, renewable energy, technology, film production, and cultural tourism, Hawaii can create a diversified economy that supports its residents and preserves its unique natural and cultural heritage. This balanced approach will help ensure that Hawaii can thrive, even if tourism faces future challenges.
